- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Developers
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create a Tile
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- OAuth for Integrations
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- IDE Plugins
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Service Management
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- APM Terms and Concepts
- Application Instrumentation
- APM Metrics Collection
- Trace Pipeline Configuration
- Correlate Traces with Other Telemetry
- Trace Explorer
- Recommendations
- Code Origins for Spans
- Service Observability
- Endpoint Observability
- Dynamic Instrumentation
- Live Debugger
- Error Tracking
- Data Security
- Guides
- Troubleshooting
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Jobs Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Quality Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Log Management
- Administration
Monitor Argo CD Deployments
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Join the Preview!
CD Visibility for Argo CD is in Preview. If you're interested in this feature, complete the form to request access.
Request AccessOverview
Argo CD is a declarative GitOps continuous delivery (CD) tool for Kubernetes. It follows the GitOps pattern by using Git repositories to define the desired application state, and automates the deployment of applications in specified target environments.
Datadog CD Visibility integrates with Argo CD by using Argo CD Notifications. Argo CD notifications consists of two main components:
- Triggers, which define when to send a notification.
- Templates, which define what to send in a notification.
Minimal setup
The setup below uses the Webhook notification service of Argo CD to send notifications to Datadog.
First, add your Datadog API Key in the argocd-notifications-secret secret with the dd-api-key key. See the Argo CD guide for information on modifying the argocd-notifications-secret.
Choose one of the following setup methods based on how you installed Argo CD:
- Regular setup (kubectl apply): For standard Argo CD installations using
kubectl apply - Helm: For Helm-based Argo CD deployments
Regular setup (kubectl apply)
Modify the argocd-notifications-cm ConfigMap to create the notification service, template, and trigger to send notifications to Datadog:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: argocd-notifications-cm
data:
service.webhook.cd-visibility-webhook: |
url: https://webhook-intake.Helm setup
If you used Helm to install Argo CD, add the following configuration to your values.yaml:
notifications:
notifiers:
service.webhook.cd-visibility-webhook: |
url: https://webhook-intake.Configuration summary
The following resources have been added:
- The
cd-visibility-webhookservice targets the Datadog intake and configures the correct headers for the request. TheDD-API-KEYheader references thedd-api-keyentry added previously in theargocd-notifications-secret. - The
cd-visibility-templatedefines what to send in the request for thecd-visibility-webhookservice. - The
cd-visibility-triggerdefines when to send the notification, and it references thecd-visibility-template.
The commit_metadata field is optional and can be used to enrich the deployment with Git information. It should be removed (together with the comma in the previous line) in the following cases:
- You are already syncing your repository information to Datadog (see Synchronize repository metadata to Datadog).
- Your Argo CD application source does not have a defined commit SHA (for example, if you are using Helm repositories).
After the notification service, trigger, and template have been added to the config map, you can subscribe any of your Argo CD applications to the integration. Modify the annotations of the Argo CD application by either using the Argo CD UI or modifying the application definition with the following annotations:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
annotations:
notifications.argoproj.io/subscribe.cd-visibility-trigger.cd-visibility-webhook: ""
dd_env: <YOUR_ENV>
dd_service: <YOUR_SERVICE>
dd_customtags: "region:us1-east, team:backend"
From the above snippet:
- The notifications annotation subscribes the Argo CD application to the notification setup created above. See the Argo CD official guide for more details on applications subscriptions.
- You can use the
dd_envannotation to configure the environment of the application. ReplaceYOUR_ENVabove with the environment to which this application is deploying (for example:stagingorprod). If you don’t set this annotation, the environment defaults tonone. - You can use the
dd_serviceannotation to configure the service of the application. ReplaceYOUR_SERVICEabove with the service that the Argo CD application is deploying (for example:transaction-service). When this annotation is used, the service name is added to all the deployment executions generated from the application. Moreover, if your service is registered in Software Catalog, the team name is also added to all the deployment executions. If your Argo CD application is configured to deploy more than one service, see Tag an Argo CD application deploying multiple services. - You can use the
dd_customtagsannotation to optionally add custom tags to the deployment executions generated for this Argo CD application. The value should be set to a comma-separated list of tags, structured askey:valuepairs.
After you have subscribed your Argo CD application by adding the annotations above, new deployments of the application will start to appear in Datadog.
The Recommended Setup section below contains recommended actions to improve the monitoring reported in CD Visibility.
Recommended setup
Change duration to wait for resources health
The duration reported in deployment events matches the sync duration in Argo CD. However, the sync duration generally represents the time spent by Argo CD to sync the Git repository state and the Kubernetes cluster state. This means that what happens after the sync (for example, the time spent by the Kubernetes resources to start up) is not included in the duration.
To change the duration reported to wait until the configured resources have started up and reached a healthy state, add a new no-op resource monitored by your Argo CD application, with a PostSync Hook annotation. The PostSync Hook will run after all the resources have reached a Healthy state, and the Argo CD sync will wait on the PostSync Hook result to update the application status as Healthy.
Below is represented an example of a PostSync Hook Job that runs a simple echo command.
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: cdvisibility-postsync-job # Ensures that the Argo CD sync duration waits for resources health
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/hook: PostSync
argocd.argoproj.io/hook-delete-policy: HookSucceeded
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: noop-echo
image: alpine:latest
command: ["echo", "all the sync resources have reached a healthy state"]
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 0
Correlate deployments with CI pipelines
By default, the Git metadata reported in deployment events is associated with the repository that Argo CD monitors. However, a common setup is to:
- Have an application repository, storing the source code, and a configuration repository, storing the Kubernetes manifests. Then, configure Argo CD to monitor the configuration repository, as outlined in the Argo CD Best Practices page.
- When a change occurs in the application repository, perform an automated commit that updates the configuration repository (for example, changing the current image of a Kubernetes resource).
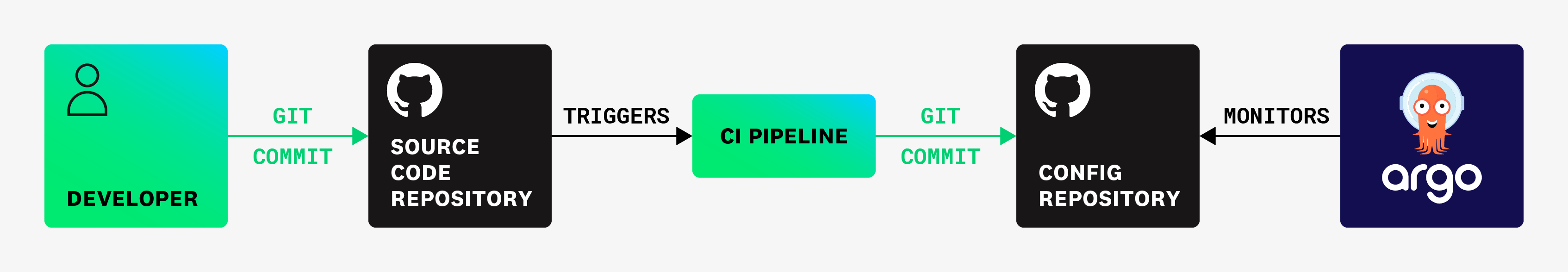
The following diagram represents an example of this kind of setup:
The datadog-ci deployment correlate-image command can be used to correlate an image with an application repository commit. When an Argo CD deployment occurs, the configuration commit information in the deployment event is replaced with the related application repository commit obtained by looking at the deployed images, if any.
To enable this correlation, you also need to add the dd_k8s_cluster annotation to your Argo CD application, specifying the name of the Kubernetes cluster that the application deploys to. The name must match the name reported in the Datadog Kubernetes product.
Here is an example on how you can run the command when generating the image that will later be deployed by Argo CD:
steps:
- name: Correlate image with Datadog
shell: bash
run: |
echo "Correlating image: ${{ inputs.image-name }} with Datadog"
datadog-ci deployment correlate-image --image ${{ inputs.image-name }} --repository-url ${{ inputs.repository-url }} --commit-sha ${{ inputs.commit-sha }}
echo "Successfully correlated ${{ inputs.image-name }} with Datadog"
This command correlates images from deployment resources. When Datadog receives a deployment, if multiple images are present and more than one of the images is correlated, Datadog takes the image that contains the service name. The correlation only works for deployment resources.
Validation
If the command has been correctly run, deployments contain Git metadata from the application repository instead of the configuration repository. Also, the deployment executions view now contains a new Pipeline tab representing the related CI pipeline trace.
Tag an Argo CD application deploying multiple services
If your Argo CD application deploys more than one service, Datadog can automatically infer the services deployed from an application sync. Datadog infers the services based on the Kubernetes resources that were modified.
Automatic service discovery is not supported when Server-Side Apply is used.
To enable automatic service tagging, you need to monitor your Kubernetes infrastructure using the Datadog Agent and your Kubernetes resources should have the following labels:
tags.datadoghq.com/service(required): specifies the Datadog service of this resource. For more information, see Unified Service Tagging.team(optional): specifies the Datadog team of this resource. If this label is omitted, the team is automatically retrieved from Software Catalog based on the service label.
Only the Kubernetes resources with the following kinds are eligible: Deployment, Rollout, ReplicaSet, StatefulSet, Service, DaemonSet, Pod, Job, and CronJob.
Add the following annotations to your Argo CD application:
dd_multiservice:true. This annotation specifies whether Datadog automatically infers the services deployed in a sync based on the changed Kubernetes resources.dd_k8s_cluster: set to the name of the Kubernetes cluster that the Argo CD application deploys to. The name must match the name reported in the Datadog Kubernetes product.
For example:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
annotations:
notifications.argoproj.io/subscribe.cd-visibility-trigger.cd-visibility-webhook: ""
dd_env: <YOUR_ENV>
dd_multiservice: true
dd_k8s_cluster: example-cluster
Visualize deployments in Datadog
The Deployments and Executions pages populate with data after a deployment has finished. For more information, see Explore CD Visibility Deployments.
Troubleshooting
If notifications are not sent, examine the logs of the argocd-notification-controller pod. The controller logs when it is sending a notification (for example: Sending notification ...) and when it fails to notify a recipient
(for example: Failed to notify recipient ...). For additional troubleshooting scenarios, see the official Argo CD documentation.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: