- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Monorepo Support in Code Coverage
This product is not supported for your selected Datadog site. ().
Overview
For large monorepos containing multiple projects or components, or where multiple teams collaborate, viewing code coverage data for the entire repository may not provide actionable insights. Code Coverage supports splitting coverage data by services and code owners, allowing you to:
- View total coverage, patch coverage, and detailed coverage data for individual services, components, or code owner teams within a monorepo
- Set up PR gates that apply to specific services or code owners
- Track coverage trends for individual services and code owner teams over time
Code Coverage automatically calculates separate coverage metrics for each service and code owner based on the file paths that belong to that service or are owned by that team.
Ways to split coverage data
Code Coverage provides two ways to split coverage data in a monorepo:
By service
- Software Catalog integration (recommended): Automatically use service definitions from Datadog Software Catalog
- Manual configuration: Define services using a YAML configuration file in your repository
By code owner
Automatically split coverage by code owner teams based on the CODEOWNERS file in your repository.
These methods can be used together. Service splitting and code owner splitting work independently—you can have coverage split by both services and code owners simultaneously. For service definitions, Software Catalog integration takes priority over manual configuration. Coverage is calculated for up to 200 services and code owners per coverage report, with a total limit of 2000 services across your organization.
Software Catalog integration
If you use Software Catalog, Code Coverage automatically uses the codeLocations attribute from your service definitions to calculate coverage for each service.
Using Software Catalog for service definitions is the recommended approach, as code locations configured in Software Catalog can be used by multiple Datadog products, including Code Coverage, Error Tracking, and Code Security. Use manual configuration only when Software Catalog integration is not available.
How Software Catalog integration works
When you define services in Software Catalog with codeLocations pointing to your repository, Code Coverage automatically:
- Reads the service definitions from Software Catalog
- Calculates coverage for each service based on the specified paths
- Displays coverage data in the Code Coverage UI
No additional configuration is needed in your repository.
Service definition example
You can add or update service definitions by adding YAML files to your repository, using the Datadog UI, enabling automatic service discovery, or importing from a third-party integration. See the Software Catalog documentation for more details.
service.datadog.yml
apiVersion: v3
kind: service
metadata:
name: checkout-service
datadog:
codeLocations:
- repositoryURL: https://github.com/my-org/my-monorepo.git
paths:
- services/checkout/**
- shared/payment/**
- shared/cart/**See the Service Definition documentation for complete details on the service definition format and available options.
Code owner-based splitting
Code Coverage can automatically split coverage data based on the CODEOWNERS file in your repository. Code owner splitting works independently from service splitting—coverage can be split by both services and code owners simultaneously.
How code owner-based splitting works
When a CODEOWNERS file is present, Code Coverage:
- Reads the code owner assignments from your repository
- Groups file paths by code owner team
- Calculates separate coverage metrics for each team’s owned code
This happens automatically without requiring any configuration file.
Requirements for code owner-based splitting
- A
CODEOWNERSfile must exist in your repository (typically at.github/CODEOWNERS,docs/CODEOWNERS, orCODEOWNERSin the root) - Source code provider integration must be configured (see Setup)
- Code owner teams must be properly formatted according to your source code provider’s requirements
Manual service configuration
Manual service configuration should only be used when you cannot use Software Catalog integration. Software Catalog is the preferred method because code locations defined there can be utilized by multiple Datadog products.
To manually define services, add a services section to the code-coverage.datadog.yml file in your repository. See Configuration for file format details, configuration options, pattern syntax, and examples.
View coverage data for services and code owners
After services or code owners are configured, coverage data becomes available filtered by service or code owner for any coverage reports uploaded after the configuration changes.
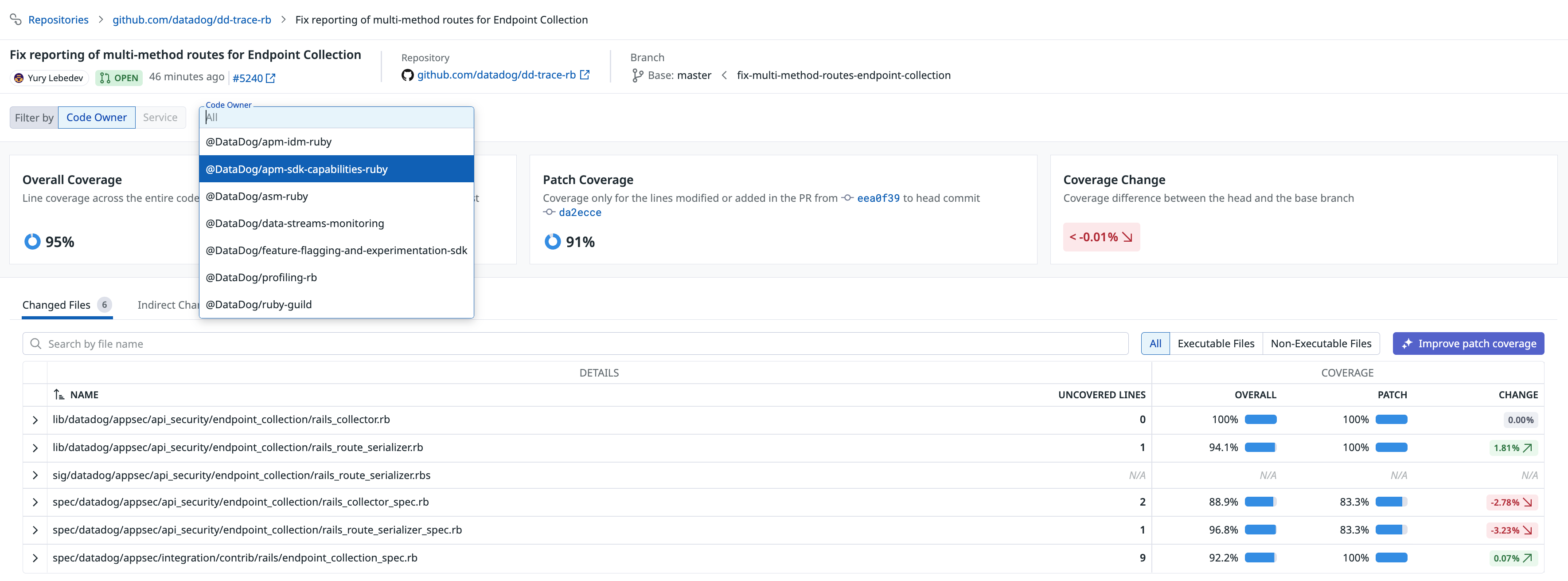
On the Branch overview, Pull Request details, and Commit details pages in Code Coverage UI, use the Code Owner or Service selector dropdown at the top to:
- View coverage metrics or detailed coverage data filtered to a specific service or code owner
- Identify which files belong to each service or are owned by specific teams
- Compare coverage across different services or code owners
- View coverage trends over time for a specific service or code owner
Set up PR Gates for services and code owners
You can configure PR Gates to enforce coverage thresholds for specific services or code owners.
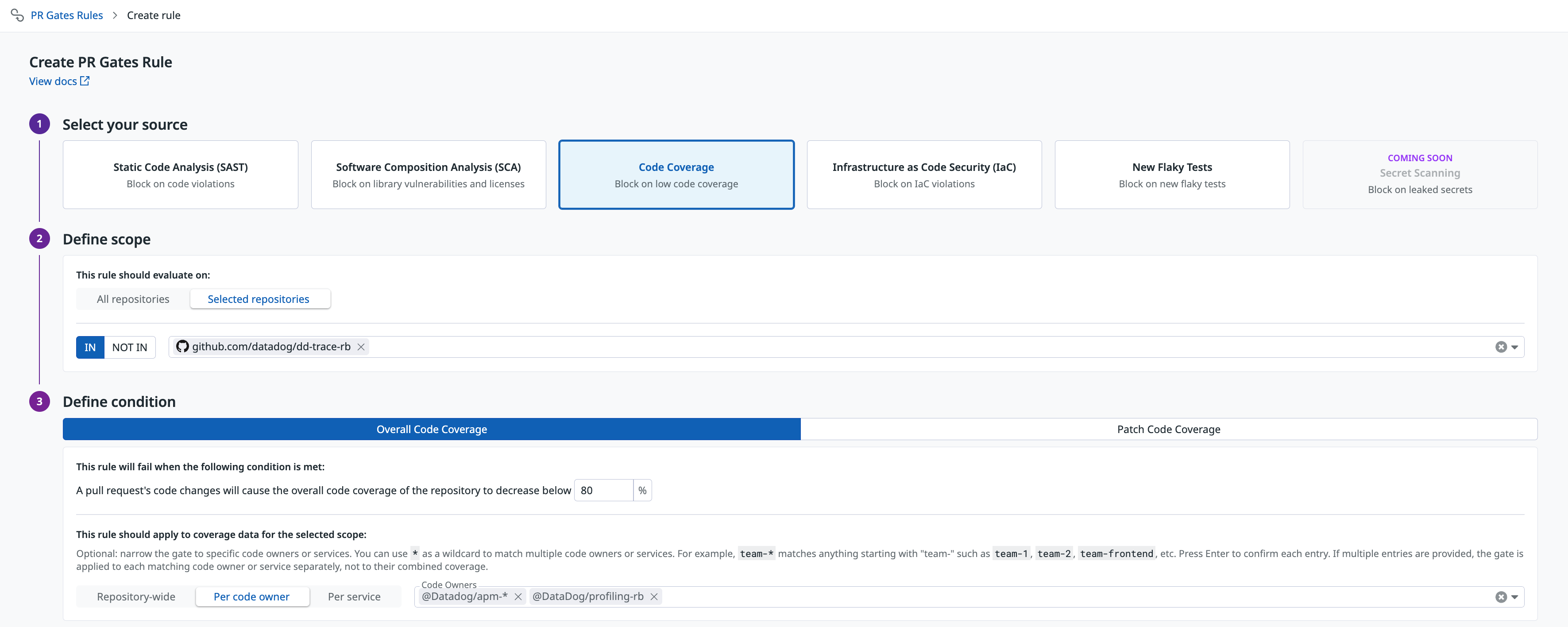
Using the Datadog UI
- Navigate to PR Gates rule creation.
- Configure the coverage threshold (total or patch coverage).
- In the per service or per code owner field, select one or more services or code owner teams the gate should apply to.
- Save the rule.
Using the YAML configuration file
You can also define service- or code owner-scoped gates directly in your code-coverage.datadog.yml file using the services and codeowners fields:
code-coverage.datadog.yml
schema-version: v1
gates:
- type: patch_coverage_percentage
config:
threshold: 90
services:
- "*"
- type: patch_coverage_percentage
config:
threshold: 95
codeowners:
- "@DataDog/backend-team"
- "@DataDog/api-*"Gates defined in the YAML file and in the Datadog UI are both evaluated when a pull request is opened or updated. See PR Gates configuration instructions for the complete YAML syntax and additional examples.
How service and code owner gates work
- With services or code owners specified: The gate evaluates coverage separately for each selected service or code owner team. When multiple services or code owners are specified, each is evaluated independently against the threshold. The gate does not combine coverage across services or code owners.
- Without services or code owners specified: The gate evaluates coverage for the entire repository.
Example configurations
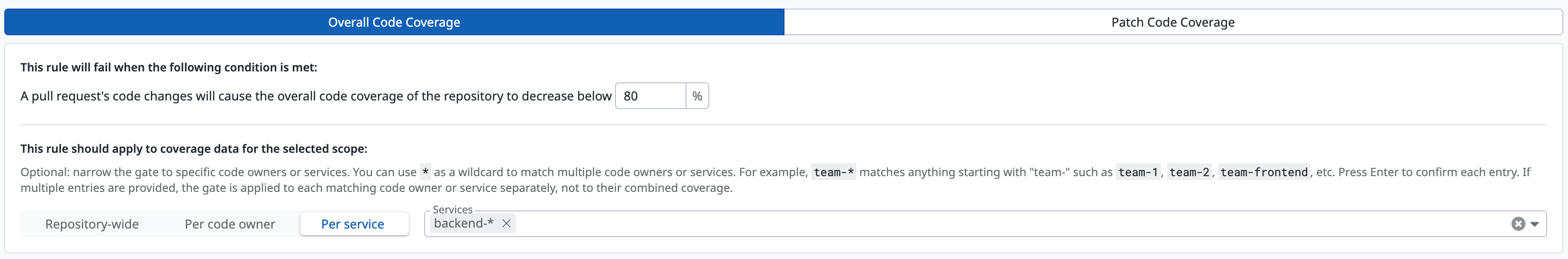
Enforce high coverage for backend services:
- Condition type:
Overall Code Coverage - Threshold:
80% - Scope:
Per service - Services:
backend-*
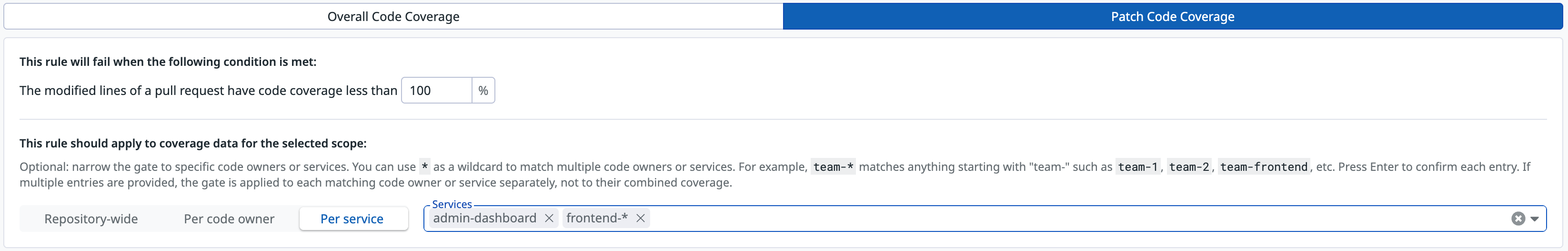
Require all new code in frontend to be tested:
- Condition type:
Patch Code Coverage - Threshold:
100% - Scope:
Per service - Services:
admin-dashboard,frontend-*
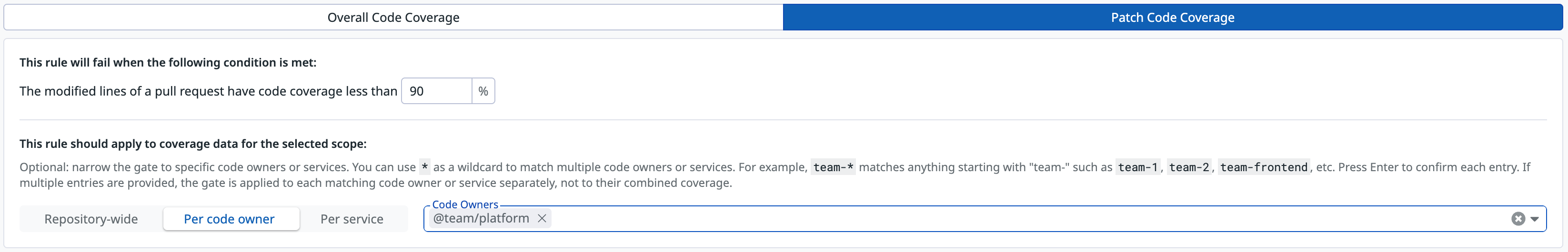
Enforce coverage for specific team’s code:
- Condition type:
Patch Code Coverage - Threshold:
90% - Scope:
Per code owner - Code owners:
@team/platform
Multiple gates per repository
You can create multiple gates for the same repository, each applying to different services or code owners. This allows you to enforce different coverage standards for different parts of your monorepo or for different teams.
Troubleshooting
Software Catalog services are not appearing in the UI
When using Software Catalog integration, changes to service definitions in Software Catalog may take up to 10 minutes to synchronize with Code Coverage. After creating or updating service definitions in Software Catalog:
- Verify that the service definition in Software Catalog includes
codeLocationswith the correctrepositoryURL. - Ensure the paths specified in
codeLocationsmatch the actual file structure. - Wait up to 10 minutes for the changes to propagate.
- Upload a new coverage report after the synchronization completes.
Software Catalog is queried when processing coverage reports, so changes only take effect for newly uploaded reports.
Manual service configuration not taking effect
If manually configured services don’t appear in the UI:
- Ensure the
code-coverage.datadog.ymlfile is at the repository root. - Validate the YAML syntax (use a YAML validator to check for errors).
- Verify that source code provider integration is properly configured (see Setup).
- Upload a new coverage report after adding or modifying the configuration file.
The configuration file is read when processing coverage reports, so changes only take effect for newly uploaded reports.
Coverage values don’t match expected service or code owner boundaries
Check that:
- Path patterns in your configuration correctly match the intended files
- Paths in coverage reports are relative to the repository root (as expected by Code Coverage)
If paths in coverage reports are relative to a subdirectory, use the --base-path option when uploading:
datadog-ci coverage upload --base-path=src .Coverage not calculated for some services or code owners
Code Coverage has the following limits:
- Per-report limit (200): Up to 200 services and code owners combined per coverage report
- Organization-wide service limit (2000): Up to 2000 services total across all repositories in your organization
If you exceed these limits, coverage is not calculated for services or code owners beyond the limit.
To stay within limits:
- Consolidate related services into broader categories.
- Remove unused or redundant service definitions.
Code owner-based coverage not appearing
Confirm that:
- A
CODEOWNERSfile exists in the standard location (.github/CODEOWNERS,docs/CODEOWNERS, orCODEOWNERSin the root) - Source code provider integration has access to read the file (see Setup)
- The code owner format follows your provider’s syntax requirements
- At least one coverage report has been uploaded after the
CODEOWNERSfile was added or updated
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: