- Essentials
- Getting Started
- Agent
- API
- APM Tracing
- Containers
- Dashboards
- Database Monitoring
- Datadog
- Datadog Site
- DevSecOps
- Incident Management
- Integrations
- Internal Developer Portal
- Logs
- Monitors
- Notebooks
- OpenTelemetry
- Profiler
- Search
- Session Replay
- Security
- Serverless for AWS Lambda
- Software Delivery
- Synthetic Monitoring and Testing
- Tags
- Workflow Automation
- Learning Center
- Support
- Glossary
- Standard Attributes
- Guides
- Agent
- Integrations
- Extend Datadog
- Authorization
- DogStatsD
- Custom Checks
- Integrations
- Build an Integration with Datadog
- Create an Agent-based Integration
- Create an API-based Integration
- Create a Log Pipeline
- Integration Assets Reference
- Build a Marketplace Offering
- Create an Integration Dashboard
- Create a Monitor Template
- Create a Cloud SIEM Detection Rule
- Install Agent Integration Developer Tool
- Service Checks
- Community
- Guides
- OpenTelemetry
- Administrator's Guide
- API
- Partners
- Datadog Mobile App
- DDSQL Reference
- CoScreen
- CoTerm
- Remote Configuration
- Cloudcraft (Standalone)
- In The App
- Dashboards
- Notebooks
- DDSQL Editor
- Reference Tables
- Sheets
- Monitors and Alerting
- Service Level Objectives
- Metrics
- Watchdog
- Bits AI
- Internal Developer Portal
- Error Tracking
- Change Tracking
- Event Management
- Incident Response
- Actions & Remediations
- Infrastructure
- Cloudcraft
- Resource Catalog
- Universal Service Monitoring
- End User Device Monitoring
- Hosts
- Containers
- Processes
- Serverless
- Network Monitoring
- Storage Management
- Cloud Cost
- Application Performance
- APM
- Continuous Profiler
- Database Monitoring
- Agent Integration Overhead
- Setup Architectures
- Setting Up Postgres
- Setting Up MySQL
- Setting Up SQL Server
- Setting Up Oracle
- Setting Up Amazon DocumentDB
- Setting Up MongoDB
- Setting Up ClickHouse
- Connecting DBM and Traces
- Data Collected
- Exploring Database Hosts
- Exploring Query Metrics
- Exploring Query Samples
- Exploring Database Schemas
- Exploring Recommendations
- Troubleshooting
- Guides
- Data Streams Monitoring
- Data Observability
- Digital Experience
- Real User Monitoring
- Synthetic Testing and Monitoring
- Continuous Testing
- Product Analytics
- Session Replay
- Software Delivery
- CI Visibility
- CD Visibility
- Deployment Gates
- Test Optimization
- Code Coverage
- PR Gates
- DORA Metrics
- Feature Flags
- Developer Integrations
- Security
- Security Overview
- Cloud SIEM
- Code Security
- Cloud Security
- App and API Protection
- AI Guard
- Workload Protection
- Sensitive Data Scanner
- AI Observability
- Log Management
- Observability Pipelines
- Configuration
- Sources
- Processors
- Destinations
- Packs
- Akamai CDN
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs
- AWS Application Load Balancer Logs
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Elastic Load Balancer Logs
- AWS Network Load Balancer Logs
- Cisco ASA
- Cloudflare
- F5
- Fastly
- Fortinet Firewall
- HAProxy Ingress
- Istio Proxy
- Juniper SRX Firewall Traffic Logs
- Netskope
- NGINX
- Okta
- Palo Alto Firewall
- Windows XML
- ZScaler ZIA DNS
- Zscaler ZIA Firewall
- Zscaler ZIA Tunnel
- Zscaler ZIA Web Logs
- Search Syntax
- Scaling and Performance
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Guides and Resources
- Log Management
- CloudPrem
- Administration
Windows
Overview
This page outlines the basic features of the Datadog Agent for Windows. If you haven’t installed the Agent yet, see the installation instructions below or follow the instructions in the app.
See Supported Platforms for the complete list of supported Windows versions.
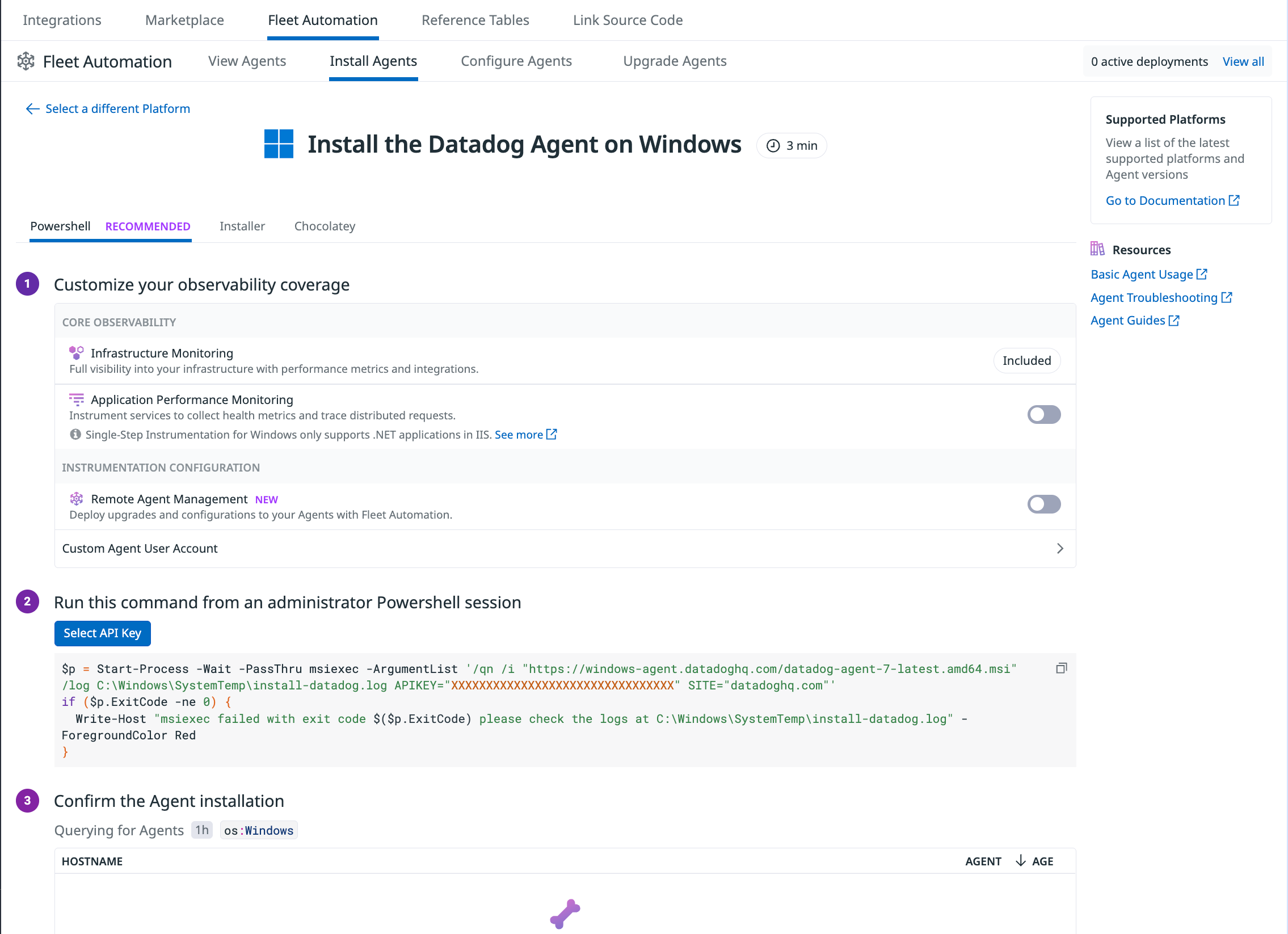
Installation
To install the Datadog Agent on your Windows hosts, follow the guided in-app flow within Fleet Automation, then copy and run the installation command. The Datadog Agents run under the ddagentuser. See Datadog Windows Agent User documentation for more information.
Alternative installation methods
Install with the Agent Manager GUI
The default installation location for the Agent is
%ProgramFiles%\Datadog\Datadog Agent. If you choose to use a custom installation location, ensure that you specify a Datadog subdirectory for the Datadog files.- Download the Datadog Agent installer to install the latest version of the Agent.
- Run the installer by opening
datadog-agent-7-latest.amd64.msi. When prompted, enter your Administrator credentials. - Follow the prompts, accept the license agreement, and enter your Datadog API key.
When the install finishes, you are given the option to launch the Datadog Agent Manager.
Installation configuration options
Each of the following configuration options can be added as a property to the command line when installing the Agent on Windows. For additional Agent configuration options, see more Agent configuration options.
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
APIKEY | String | Adds the Datadog API KEY to the configuration file. |
SITE | String | Set the Datadog intake site, for example: SITE=datadoghq.com |
TAGS | String | Comma-separated list of tags to assign in the configuration file. Example: TAGS="key_1:val_1,key_2:val_2" |
HOSTNAME | String | Configures the hostname reported by the Agent to Datadog (overrides any hostname calculated at runtime). |
DDAGENTUSER_NAME | String | Override the default ddagentuser username used during Agent installation (v6.11.0+). Learn more about the Datadog Windows Agent User. |
DDAGENTUSER_PASSWORD | String | Override the cryptographically secure password generated for the ddagentuser user during Agent installation (v6.11.0+). Must be provided for installs on domain servers. Learn more about the Datadog Windows Agent User. |
APPLICATIONDATADIRECTORY | Path | Override the directory to use for the configuration file directory tree. May only be provided on initial install; not valid for upgrades. Default: C:\ProgramData\Datadog. (v6.11.0+) |
PROJECTLOCATION | Path | Override the directory to use for the binary file directory tree. May only be provided on initial install; not valid for upgrades. Default: %ProgramFiles%\Datadog\Datadog Agent. (v6.11.0+)If you choose to override the default directory, ensure that you specify a Datadog subdirectory for the Datadog files. |
Notes
- The
/qnoption runs a quiet install. To see the GUI prompts, remove it. - Some Agent versions may cause a forced reboot. To prevent this, add the parameter:
REBOOT=ReallySuppress. - Some Agent components require a kernel driver to collect data. To know if a kernel driver is required for your component, see its documentation page or search for
kernel driverin the associated Agent configuration files. - If a valid
datadog.yamlis found, that file takes precedence over all specified command line options.
More Agent configuration options
Each of the following configuration options can be added as a property to the command line when installing the Agent on Windows.
Note: If a valid datadog.yaml is found, that file takes precedence over all specified command line options.
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
LOGS_ENABLED | String | Enable ("true") or disable ("false") the log collection feature in the configuration file. Logs are disabled by default. |
APM_ENABLED | String | Enable ("true") or disable ("false") the APM Agent in the configuration file. APM is enabled by default. |
PROCESS_ENABLED | String | Enable ("true") or disable ("false") the Process Agent in the configuration file. The Process Agent is disabled by default. |
HOSTNAME_FQDN_ENABLED | String | Enable ("true") or disable ("false") the usage of FQDN for the Agent hostname. It is equivalent to set hostname_fqdn in the Agent configuration file. The usage of FQDN for the hostname is disabled by default. (v6.20.0+) |
CMD_PORT | Number | A valid port number between 0 and 65534. The Datadog Agent exposes a command API on port 5001. If that port is already in use by another program, the default may be overridden here. |
PROXY_HOST | String | (If using a proxy) sets your proxy host. Learn more about using a proxy with the Datadog Agent. |
PROXY_PORT | Number | (If using a proxy) sets your proxy port. Learn more about using a proxy with the Datadog Agent. |
PROXY_USER | String | (If using a proxy) sets your proxy user. Learn more about using a proxy with the Datadog Agent. |
PROXY_PASSWORD | String | (If using a proxy) sets your proxy password. For the process/container Agent, this variable is required for passing in an authentication password and cannot be renamed. Learn more about using a proxy with the Datadog Agent. |
EC2_USE_WINDOWS_PREFIX_DETECTION | Boolean | Use the EC2 instance id for Windows hosts on EC2. (v7.28.0+) |
Installation log files
Set the /log <FILENAME> msiexec option to configure an installation log file. If this option is not set, msiexec writes the log to %TEMP%\MSI*.LOG by default.
Configuration
The main Agent configuration file is located at
C:\ProgramData\Datadog\datadog.yaml. This file is used for host-wide settings such as the API key, selected Datadog site, proxy parameters, host tags, and log level.
There is also a datadog.yaml.example file in the same directory, which is a fully commented reference with all available configuration options, useful for reference and copying specific settings.
Configuration files for integrations are in:
C:\ProgramData\Datadog\conf.d\ There may also be an alternative legacy location: C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Datadog\conf.d\.
Each integration has a subdirectory <INTEGRATION>.d\ that contains:
conf.yaml: The active settings for the integration
conf.yaml.example: A sample file showing what configuration keys are supported
When making configuration changes, be sure to restart the Agent to ensure the changes take effect.
The Datadog Agent Manager GUI can be used to enable, disable, and configure checks. You must restart the Agent for your changes to take effect.
Note: ProgramData is a hidden folder.
Agent commands
The execution of the Agent is controlled by the Windows Service Control Manager.
- The main executable name is
agent.exe. - The configuration GUI is a browser-based configuration application (for Windows 64-bit only).
- Commands can be run from the elevated (run as Admin) command line (PowerShell or Command Prompt) using the syntax
<PATH_TO_AGENT.EXE> <COMMAND>. - Command-line options are below:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| check | Runs the specified check. |
| diagnose | Executes some connectivity diagnosis on your system. |
| flare | Collects a flare and send it to Datadog. |
| help | Gets help about any command. |
| hostname | Prints the hostname used by the Agent. |
| import | Imports and converts configuration files from previous versions of the Agent. |
| launch-gui | Starts the Datadog Agent Manager. |
| restart-service | Restarts the Agent within the service control manager. |
| run | Starts the Agent. |
| start | Starts the Agent. (Being deprecated, but accepted. Use run as an alternative.) |
| start-service | Starts the Agent within the service control manager. |
| status | Print the current status. |
| stopservice | Stops the Agent within the service control manager. |
| version | Prints the version info. |
Examples:
PowerShell (
powershell.exe)& "$env:ProgramFiles\Datadog\Datadog Agent\bin\agent.exe" status & "$env:ProgramFiles\Datadog\Datadog Agent\bin\agent.exe" launch-gui & "$env:ProgramFiles\Datadog\Datadog Agent\bin\agent.exe" flareCommand Prompt (
cmd.exe)"%ProgramFiles%\Datadog\Datadog Agent\bin\agent.exe" status "%ProgramFiles%\Datadog\Datadog Agent\bin\agent.exe" launch-gui "%ProgramFiles%\Datadog\Datadog Agent\bin\agent.exe" flare
Uninstall the Agent
There are two different methods to uninstall the Agent on Windows. Both methods remove the Agent, but do not remove the C:\ProgramData\Datadog configuration folder on the host.
Add or remove programs
- Press CTRL and Esc or use the Windows key to run Windows Search.
- Search for
addand click Add or remove programs. - Search for
Datadog Agentand click Uninstall.
PowerShell
Note: Enable WinRM to use the commands below.
Use the following PowerShell command to uninstall the Agent without rebooting:
$productCode = (@(Get-ChildItem -Path "HKLM:SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall" -Recurse) | Where {$_.GetValue("DisplayName") -like "Datadog Agent" }).PSChildName
start-process msiexec -Wait -ArgumentList ('/log', 'C:\uninst.log', '/q', '/x', "$productCode", 'REBOOT=ReallySuppress')Troubleshooting
For troubleshooting steps, see the Agent Troubleshooting documentation .
Agent status and information
To verify the Agent is running, check if the DatadogAgent service in the Services panel is listed as Started. A process called Datadog Metrics Agent (agent.exe) should also exist in the Task Manager.
To receive more information about the Agent’s state, start the Datadog Agent Manager:
- Right click on the Datadog Agent system tray icon -> Configure, or
- Run
launch-guicommand from an elevated(run as Admin) command line- PowerShell:
& "<PATH_TO_AGENT.EXE>" launch-gui - cmd:
"<PATH_TO_AGENT.EXE>" launch-gui
- PowerShell:
Then, open the status page by going to Status -> General. Get more information on running checks in Status -> Collector and Checks -> Summary.
The status command is available for PowerShell:
& "$env:ProgramFiles\Datadog\Datadog Agent\bin\agent.exe" status
or cmd.exe:
"%ProgramFiles%\Datadog\Datadog Agent\bin\agent.exe" status
Logs location
The Agent logs are located in C:\ProgramData\Datadog\logs\agent.log.
Note: ProgramData is a hidden folder.
Use cases
Monitoring a Windows service
On your target host, launch the Datadog Agent Manager and select the “Windows Service” integration from the list. There is an out-of-the-box example; however, this example uses DHCP.
To get the name of the service, open services.msc and locate your target service. Using DHCP as the target, you can see the service name at the top of the service properties window:
When adding your own services, be sure to follow the formatting exactly as shown. If formatting is not correct the integration fails. Note: Special characters in a service name must be escaped. For example, the name MSSQL$BILLING can be added with MSSQL\$BILLING.
Also, whenever you modify an integration, the Datadog service needs to be restarted. You can do this from services.msc or from the UI sidebar.
For Services, Datadog doesn’t track the metrics—only their availability. (For metrics, use the Process or WMI integration). To set up a Monitor, select the Integration monitor type then search for Windows Service. From Integration Status -> Pick Monitor Scope, choose the service you would like to monitor.
Monitoring system load for Windows
The Datadog Agent collects a large number of system metrics by default. The most commonly used system metrics are system.load.* but these metrics are Unix specific.
While Windows does not offer the system.load.* metrics, an equivalent option that’s available by default is system.proc.queue.length. This metric shows the number of threads observed as delayed in the processor ready queue that are waiting to be executed.
Monitoring Windows processes
You can monitor Windows processes with Live Process Monitoring. To enable this on Windows, edit the Agent main configuration file by setting the following parameter to true:
datadog.yaml:
process_config:
enabled: "true"
After configuration is complete, restart the Agent.
Further reading
Additional helpful documentation, links, and articles: